Why Every Family Needs to Prioritize Executive Functioning
The Importance of Executive Functioning
- Unlock Success: Executive Functioning is the key skill set that helps students succeed.
- Life Skills: Teaches prioritization, organization, and time management, essential for school and adulthood.
- Expert Guidance: The House is the only tutoring company in the area with tutors trained in Executive Functioning best practices.
- Personalized Support: Our unique approach ensures each student receives the guidance they need to thrive.
Free Assessment: Wondering where to start? Take our Free Executive Functioning Assessment.


Executive Functioning is a key factor of your child’s success that they don’t typically teach in school. That’s where we come in.
The House has partnered with MetaCog to offer a free assessment so parents and our tutors get to know where your student stands and where they may need additional guidance. And it only takes approximately 10 minutes to complete.

What Exactly are Executive Functioning skills?
These cognitive skills are what allow students to plan and complete tasks that are essential for success in school and beyond.
In short, Executive Functioning skills are the skills that help us organize our thoughts, pay attention, plan, and manage our time effectively. Our assessment allows us to identify your student’s strengths and target weaknesses, and curate a tutoring plan based on how they set goals, think flexibly, organize their time, manage their materials, and access memory. The data can also be used to personalize strategies for individual students and inform goals for their IEPs and 504 Plans (if applicable).
Benefits of strong executive functioning skills:
Improved academic performance
Students with strong executive functioning skills are better able to organize their time, prioritize their work, and focus on their goals. This can lead to improved grades, higher test scores, and more efficient studying. Oh, and confidence!
Better social relationships
Executive functioning skills are important for regulating emotions, reading social cues, and making good decisions. Students who are able to regulate their behavior and emotions are more likely to have positive social relationships with their peers, teachers, and family members.
Increased independence
Strong executive functioning skills help individuals become more independent and self-sufficient. They are better able to manage their time, complete tasks on their own, and make decisions that are in their best interest. Peer pressure will be less of an influence.
Improved mental health
Executive functioning skills are important for managing stress, regulating emotions, and problem-solving. Individuals with strong executive functioning skills are better able to cope with challenges and setbacks, which can lead to improved mental health and well-being.

How Parents Can Help
It’s important to remember that Executive Functioning skills build over time, not overnight. One way to support your student is to help them make a schedule or to-do list to help them move toward goals, and then adjust as new priorities emerge. This can help them plan and prioritize tasks, and alleviate stress. For additional support, we offer free in-lounge planning sessions during the school year from 12:30 - 3:30 PM on Sundays. Our tutors can help your student plan the week ahead to reduce stress for the whole family.
More About Our Executive Functioning Assessment
The curriculum was created by the Research Institute for Learning and Development and is based on research by Dr. Meltzer.
The surveys are a convenient and practical way to collect information on your child’s EF strategy use and motivation – even at multiple times throughout the year to track growth and customize their executive function instruction.
With our assessments, students develop the self-understanding to know which strategies work best for them as they complete their homework, plan long-term projects, and study for tests. Tutoring sessions can be specifically aligned with our lessons depending on what your student’s strengths and challenges are.
- STRATUS Assessment (Strategy Use): This assessment highlights a student’s understanding of their use of planning, organizing, memorizing, shifting, and self-checking strategies
- Approx 10 minutes to complete
- ME Assessment (Motivation & Effort): This assessment helps us to understand what motivates a student and allows for a narrative piece written by the student to share how much effort they put into various subjects and academic tasks, as well as what helps them to persevere when they are challenged
- Approx 20 minutes to complete
- We recommend administering surveys throughout the school year to see where a student is progressing and what new strengths/challenges may arise.

DEFINITIONS:
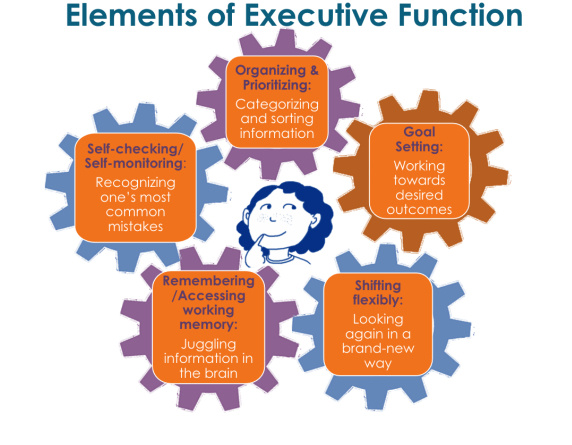
- Executive Function: Executive function (EF) is a broad term used to describe the complex cognitive processes that are the foundation for flexible, goal-directed behaviors. Key EF processes include shifting flexibly (cognitive flexibility), goal setting, organizing and prioritizing, accessing working memory, as well as self-monitoring and self-checking
- Metacognition: “Thinking about one’s own thinking”. Self- understanding is the foundation of metacognition. There are three key processes involved in metacognition: (1) Self-understanding - understanding our unique profiles of strengths and challenges; (2) Reflection - thinking about what we know about ourselves and what strategies can help us to learn; and (3) Self- regulation - regulating and monitoring our learning. Together, these comprise important learning processes.
- Goal Setting: Goal Setting refers to the ability to identify a desired outcome based on understanding of personal strengths and challenges. In order to meet a goal, students need to carefully organize their approach by considering both the”big picture” and the smaller steps involved.
- Cognitive Flexibility: Cognitive Flexibility is the ability to think flexibly and to shift perspectives and approaches. This process helps students to shift flexibly between major themes and details as well as to differentiate relevant information from irrelevant information. Cognitive flexibility is crucial for learning new concepts, solving problems, and understanding the perspective of others.
- Organization: Organization involves the creation of a meaningful structure for ordering parts into a cohesive whole. Strategies for organizing and prioritizing systematically help students to achieve their goals
- Working Memory: Working memory is the ability to hold information in one’s mind and to mentally manipulate this information (e.g., mental math).
- Short-Term Memory: Information received from the five senses is stored in short-term memory. This is retained for a short period of time before the information is either stored in long-term memory or forgotten.
- Long-Term Memory: Long-term memory is the storage house for the brain; important information is stored for longer periods of time.
- Self-Monitoring: Self-monitoring refers to the process of reflecting and using strategies to track performance and outcomes. Self-monitoring strategies allow students to check the effectiveness of their strategy use, to evaluate and revise their strategy use, and to continuously adjust their use of strategies according to the task and situation demands.
- Self-Checking: Self-checking occurs either during an academic task or after an academic task has been completed. Students must carefully review and check assignments using their knowledge of the common errors they often make.

.png?width=569&height=296&name=Group%2060%20(1).png)
